PASBADIA
Patient-oriented smartphone-based diagnostics
In the joint PASBADIA project, the expertise of the successful cross-university competence centre TANDEM (Technology and Engineering in Medicine) between the Technical University Lübeck, the University of Lübeck, and COPICOH will be brought together for the first time. A collaboration of engineers, natural scientists and practising physicians jointly research to develop new artificial intelligence (AI) based smartphone-supported patient-oriented diagnostic procedures.
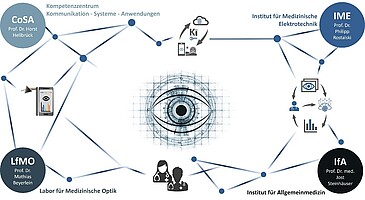
In medicine, rapid diagnosis near the patient is often necessary, for example, when screening for chronic diseases or monitoring the curative course of patients with mobility impairments in rural areas. In poorly accessible or under-served areas, the use of readily available diagnostic equipment is a promising approach to improve access to medical care. With the increasing computational performance of edge devices and the rising availability of built-in sensor technology, current smartphones and micro-computers provide a suitable, low-cost solution for this task.
Exemplary, smartphone built-in high-quality cameras, allow the implementation of optical diagnostic procedures from the field of classic devices, provided that appropriate attachments are adapted to the smartphone and measurement data is evaluated on-site.
Video: PASBADIA – Transdisciplinary collaboration for the benefit of patients
Over four years, four doctoral students work with master’s students to develop mobile multispectral imaging devices used as diagnostic tools in general medicine to enable ophthalmological examinations for which special optical devices would otherwise be required. To support general practitioners on-site with the detection and diagnosis of vision-threatening eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma, a distributed AI-based evaluation of the retinal images is implemented enabling automatic diagnosis with high performance. As part of the project, also the extent to which a family doctor can support ophthalmological care in rural areas with such an AI-supported diagnostic tool is being investigated.
At the Institute of Electrical Engineering in Medicine (IME), an efficient, mobile-device applicable and transparent, data-driven analysis algorithm for the detection of eye diseases with high diagnostic performance is researched based on the retinal data captured by the mobile imaging device. To this end, modern methods of statistical learning theory, i.e. deep learning, and Bayesian inference are used to train uncertainty-aware models which can explain their decision to the practitioner and hence improve the interpretability and trustworthiness of the AI algorithm.
The joint PASBADIA project of the two Lübeck universities is kindly supported by the Joachim Herz Foundation in Hamburg with about 1.3 million euros.
More details about PASBADIA:
News and Activities:
Members
Philipp Rostalski

Gebäude 19
philipp.rostalski(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 3101 6200
Marlin Siebert

Gebäude 19
m.siebert(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 3101 6220







